
When your application scales from hundreds to millions of users, database performance becomes the critical bottleneck that determines success or failure. A poorly optimized database can transform a promising platform into a frustratingly slow experience, driving users away before they ever engage with your core features. Understanding and implementing advanced database optimization techniques isn’t just about improving speed—it’s about building sustainable infrastructure that grows with your business.
The Performance Crisis in Modern Applications
High-traffic applications face unique challenges that don’t exist at smaller scales. What works perfectly for ten thousand users often collapses spectacularly at one million. Database queries that execute in milliseconds during development suddenly timeout in production. Connection pools exhaust themselves. Memory consumption spirals out of control. These aren’t theoretical problems—they’re real barriers that organizations face daily as they scale.
The cost of poor database performance extends beyond user experience. Slow queries consume more server resources, requiring expensive horizontal scaling before it’s truly necessary. They create cascading failures across microservices architectures. They complicate debugging and monitoring. Most critically, they compound over time, with each new feature adding incremental load until the entire system reaches a breaking point.
Indexing Strategies That Actually Work
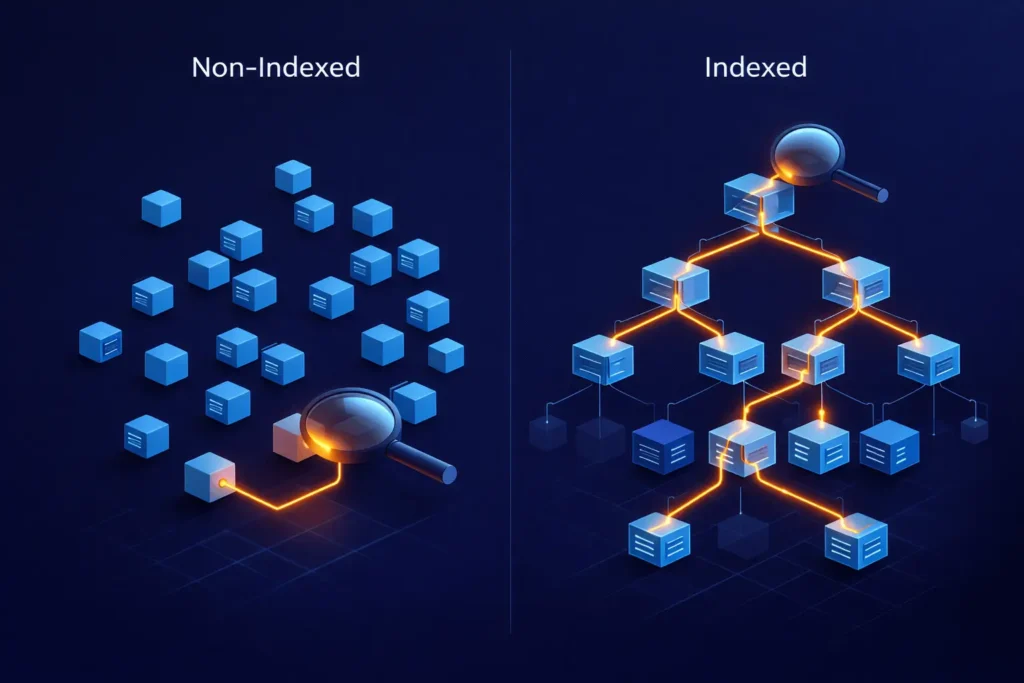
Database indexing represents the foundation of query optimization, yet it remains one of the most misunderstood aspects of database design. The naive approach—adding indexes to every column used in WHERE clauses—creates more problems than it solves. Each index adds overhead to write operations and consumes valuable memory and storage space.
Effective indexing begins with understanding your query patterns. Analyze slow query logs to identify the most frequently executed and slowest queries. Focus optimization efforts on queries that appear in hot code paths—those executed hundreds or thousands of times per second. For these critical queries, composite indexes that match the exact filter and sort order can reduce execution time from seconds to milliseconds.
B-tree indexes excel for range queries and sorting operations, making them ideal for timestamp-based queries common in high-traffic applications. Hash indexes provide faster lookups for equality comparisons but can’t support range queries. Partial indexes, which index only a subset of rows meeting specific criteria, dramatically reduce index size while maintaining performance for targeted query patterns.
Consider a social media feed query filtering posts by user_id and ordering by created_at. A composite index on (user_id, created_at DESC) eliminates the need for sorting and enables index-only scans. However, adding a status column filter requires careful consideration—extending the index versus using index intersection techniques depends on data distribution and query frequency.
Query Optimization Beyond the Basics
Writing efficient SQL requires thinking like the database optimizer. Understanding execution plans reveals how databases actually process your queries, exposing hidden table scans, inefficient joins, and missing indexes. Modern databases provide sophisticated EXPLAIN commands that show the optimizer’s decision-making process, but interpreting these plans requires expertise.
Join order matters enormously in multi-table queries. Databases attempt to optimize join sequences automatically, but explicitly structuring queries to join smaller result sets first reduces intermediate data volumes. Using INNER JOINs instead of subqueries often improves performance, as optimizers can reorder joins but struggle to optimize correlated subqueries.
Avoiding SELECT * might seem obvious, but its impact multiplies at scale. Fetching unnecessary columns wastes network bandwidth, memory, and cache space. In columnar databases, selecting specific columns allows the database to read only relevant column files. Even in row-oriented databases, smaller result sets mean more rows fit in memory buffers.
N+1 query problems plague ORM-based applications, where a single query to fetch records triggers additional queries for each record’s relationships. Eager loading strategies and JOIN operations eliminate these redundant round-trips. In microservices architectures, batching database requests prevents chatty communication patterns that destroy performance under load.
Caching Strategies for Maximum Impact
Caching represents the most effective optimization technique for read-heavy workloads, but naive caching implementations introduce subtle bugs and consistency problems. Multi-layer caching strategies balance hit rates, complexity, and consistency requirements.
Application-level caching with Redis or Memcached offloads repetitive queries entirely. For high-traffic applications, cache hit rates above 95% can reduce database load by an order of magnitude. However, cache invalidation remains computer science’s hardest problem. Time-based expiration works for data that tolerates eventual consistency, while event-based invalidation maintains stricter consistency guarantees at the cost of complexity.
Query result caching at the database level provides transparent optimization for identical queries. PostgreSQL and MySQL maintain internal query caches, though their effectiveness depends on query patterns and parameter binding. Prepared statements improve cache utilization by separating query structure from parameters.
Materialized views precompute expensive aggregations and joins, trading storage space and update complexity for query performance. For analytics queries that scan millions of rows, materialized views can reduce execution time from minutes to seconds. Incremental refresh strategies minimize update overhead, making materialized views viable even for frequently updated data.
Connection Pooling and Resource Management
Database connections represent expensive resources that require careful management. Creating new connections involves TCP handshakes, authentication, and session initialization—overhead that becomes prohibitive when multiplied across thousands of requests per second. Connection pooling amortizes this cost by maintaining persistent connections that application threads reuse.
Optimal pool sizing depends on database capabilities and application concurrency. Too few connections create bottlenecks as threads wait for available connections. Too many connections overwhelm the database, consuming memory for connection buffers and reducing CPU efficiency through context switching. A common starting point uses pool size equal to (core_count × 2) + effective_spindle_count, but load testing under realistic conditions determines actual requirements.
Connection pool exhaustion indicates scaling problems that connection pool configuration alone cannot solve. Implementing timeouts prevents threads from waiting indefinitely for connections. Circuit breakers detect database failures early, preventing cascade failures across distributed systems. These reliability patterns transform catastrophic failures into graceful degradation.
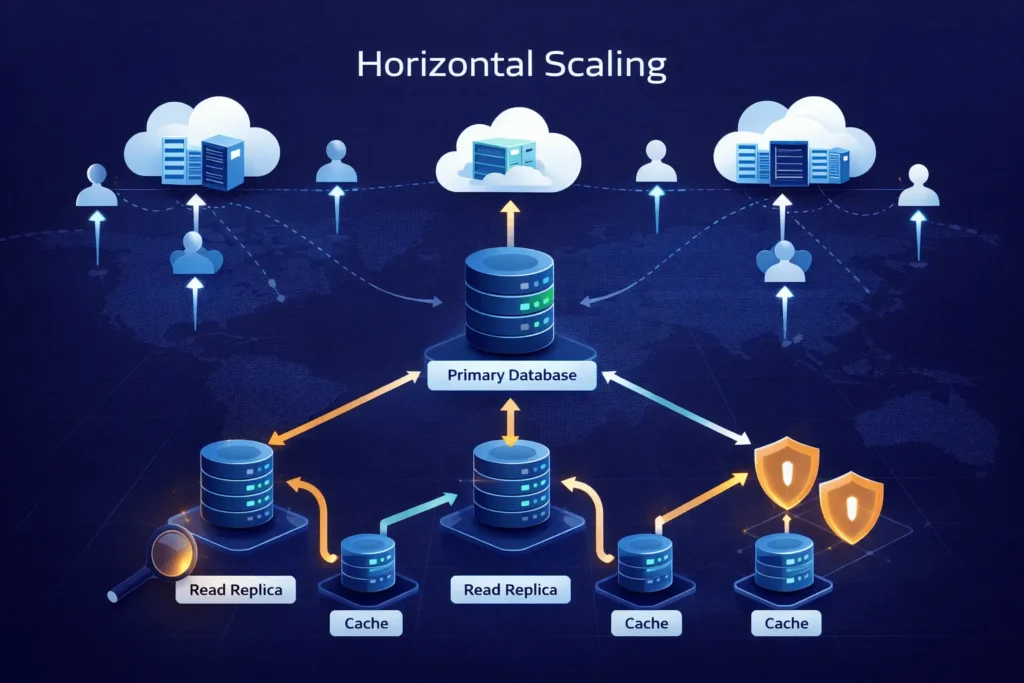
Horizontal Scaling and Sharding
When vertical scaling reaches physical limits, horizontal scaling distributes load across multiple database instances. Read replicas handle read-heavy workloads by offloading SELECT queries from the primary database. Asynchronous replication introduces eventual consistency, requiring applications to tolerate slight replication lag.
Sharding partitions data across multiple databases based on shard keys. User-based sharding routes all data for specific users to dedicated shards, ensuring queries accessing user data hit single shards. Geographic sharding places data closer to users, reducing latency for global applications. Range-based sharding distributes data by value ranges, though uneven distribution creates hot spots.
Implementing sharding requires fundamental application architecture changes. Cross-shard queries become expensive or impossible, requiring denormalization and data duplication. Transactions spanning multiple shards need distributed transaction protocols or eventual consistency patterns. These trade-offs make sharding a last resort after exhausting other optimization techniques.
Monitoring and Continuous Database Optimization
Database optimization isn’t a one-time project but an ongoing process. Query patterns evolve as applications add features and user behavior changes. Establishing comprehensive monitoring identifies performance degradation before it impacts users.
Slow query logs capture queries exceeding thresholds, revealing optimization opportunities. Tracking query execution counts identifies high-frequency queries deserving optimization attention. Database performance metrics—CPU utilization, memory usage, disk I/O, connection counts—provide early warning signals for capacity problems.
Modern observability platforms correlate application performance with database metrics, connecting slow API endpoints to specific queries. Distributed tracing reveals database calls within request flows, exposing opportunities for batching, caching, or parallelization. This data-driven approach ensures optimization efforts focus on actual bottlenecks rather than premature optimization.
Building high-performance databases for high-traffic applications demands technical expertise, systematic methodology, and continuous refinement. The techniques outlined here provide a foundation, but every application presents unique challenges requiring customized solutions. Success comes from understanding fundamental principles, measuring actual performance, and iterating based on real-world results.





